
Background of the study
Phosphorus is an important nutrient element that is widely found in all living organisms and plays a key role in ecosystems. Eutrophication of water bodies caused by excessive phosphorus discharge not only affects water quality and destroys ecosystems, but also may cause a series of environmental and health problems.
Therefore, the development of more efficient, stable and economical phosphorus removal technologies remains an urgent issue.
Introduction
Recently, Professor Feng Congjun of Beijing University of Chemical Technology led a research team to develop a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method to prepare three flower-like porous proposed thin hydrotalcite materials, and investigated in detail their adsorption behaviors of phosphate in aqueous solution.
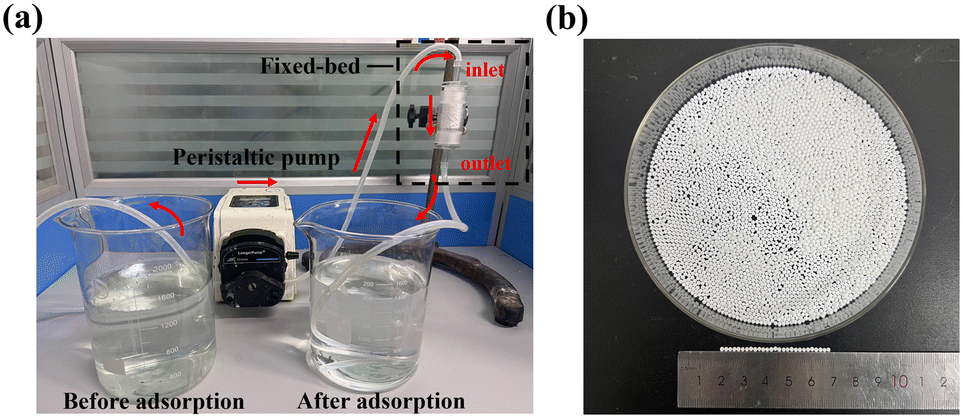
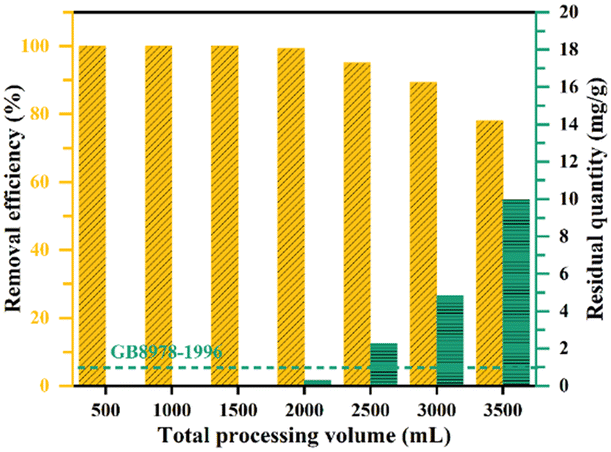
This work controlled the morphology of the materials by adjusting the feeding ratio of aluminum salt to alkali in the reaction system, resulting in different pore structures as well as different degrees of (020) crystal surface exposure. The adsorption of phosphate on all the samples conformed to the Elovich kinetic model and the Langmuir adsorption isotherm model. The high percentage of aluminum salt doping increased the specific surface area by 32.7% and increased the percentage of (020) crystal surface exposure by 59.6%. Among the three samples, sample A-1/10 prepared at a molar ratio of Al³⁺ to NaOH of 1:10 had the largest specific surface area (430.67 m² g-¹) and the highest percentage of (020) crystalline surface exposure (19.25%). Sample A-1/10 showed excellent phosphate removal performance in acidic solution with a maximum adsorption capacity of 158.58 mg g-¹. In addition, a fixed-bed adsorption column was constructed using sodium alginate-assisted molding of anthropomorphic thin hydrotalcite spheres, which could remove 95% of the phosphate in water. These results indicate that this material has a promising future for the practical application of phosphate removal in water.
The results are summarized as “Microwave-assisted fabrication of porous flowerlike pseudo-boehmite and high-efficiency phosphate removal from water: batch and fixed bed column continuous operation”. Microwave-assisted fabrication of porous flowerlike pseudo-boehmite and high-efficiency phosphate removal from water: batch and fixed bed column continuous operation" was published in Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, a journal of the Royal Society of Chemistry. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology.

