For cholestatic liver injury (CLI), the team of Beijing University of Chemical Technology designed an enzyme responsive fluoropeptide, which was assembled under the induction of alkaline phosphatase. The diagnosis was achieved by detecting the 19F NMR signal in the urine of CLI mice. It can also be used for treatment, providing a new idea for the molecular design of integrated diagnosis and treatment polypeptides.
Cholestasis type liver injury (CLI) is caused by bile secretion and excretion disorders. Clinical diagnosis often relies on serum screening and final diagnosis through biopsy. In contrast, urine analysis diagnosis is a convenient non-invasive diagnostic method, which is characterized by easy collection of samples and the changes of some components can sensitively reflect the physiological or pathological changes of the body. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop the detection of cholestatic liver injury based on urine detection.
Since there are almost no fluorinated molecules in human body, only a small amount of fluorinated substances exist in bones or teeth in solid form. be based on nineteen F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) analysis and detection method has the advantage of no endogenous interference, which can greatly improve the specificity of disease detection. Based on this characteristic, people have developed a method for the analysis of fluorinated drugs in urine, and also designed a fluorinated probe suitable for the detection of disease markers in urine samples. However, there is no fluorine-containing probe that can be used for in vivo biotransformation to convert pathological and biochemical information into nineteen F NMR signal, and disease diagnosis is realized through urine analysis.
Based on this, Professor Wang Leyu and Professor Xu Suying of Beijing University of Chemical Technology Team, By using the flexible and adjustable structure and rich recognizable sites of polypeptide molecules, an enzyme responsive fluoropeptide was designed and synthesized to regulate the pharmacokinetics of fluoropeptide in vivo through enzyme responsive assembly nineteen F NMR signal strength to realize the urine analysis and diagnosis of CLI. Related work was published in the title of "Design of Fluorinated Peptides as Biotransformed Urinalysis Biomarkers for Non Invasive Diagnosis and Treatment of Life Injury through Energy Directed Kinetics"《 Advanced Materials 》On.

The author designed Tyr (H two PO three )-Phe-Thr-Glu-Phe(Y P FTEF) fluorinated polypeptide, which is induced by alkaline phosphatase (ALP) overexpressed at the focus to form a large assembly and prolong its metabolic time in vivo. After intravenous injection of fluoride containing polypeptide nineteen The hysteresis of F NMR signal peak value realizes the nineteen F NMR urine analysis (Figure 1).
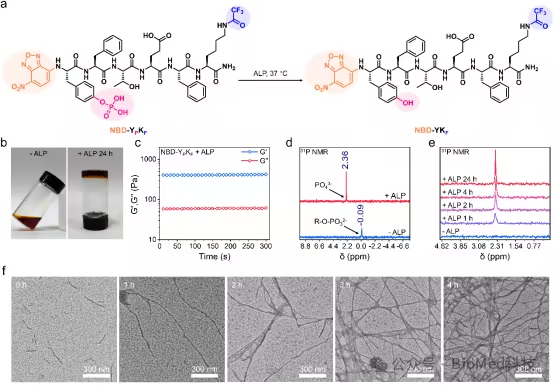
Figure 1 Design and nineteen Schematic diagram of F NMR urine analysis
The author first verified the enzymatic response assembly characteristics of fluoropeptides in vitro (Fig. 2). After being treated with ALP, the solution of fluoride containing polypeptide gradually turns into hydrogel, thirty-one The chemical shift of P NMR changed from 0.09 ppm to 2.36 ppm, indicating that ALP induced the departure of the phosphate group in the fluorinated polypeptide molecule. Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images also confirmed the formation of polypeptide hydrogels.

Fig. 2 Enzyme response assembly of fluoropeptides
Fluorine containing peptides have a specific response to ALP. The mixed structure of alpha helix and beta fold mainly exists in the fluorinated peptides treated with ALP, and it is accompanied by an increase in size and Zeta potential. At the same time, the fluorogenic probe has good biocompatibility, and no obvious cytotoxicity of fluorogenic polypeptide was observed through cytotoxicity test (Figure 3).
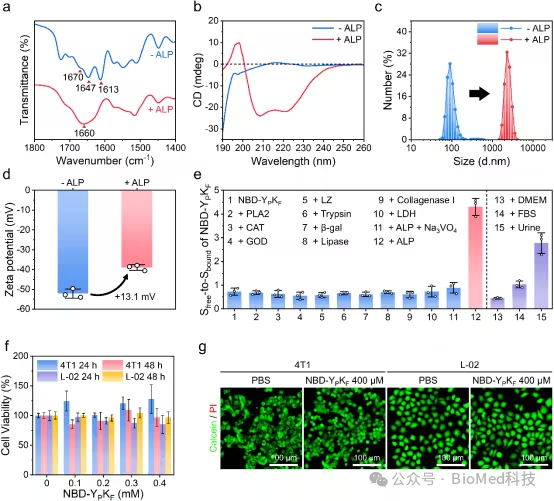
Fig. 3 Enzyme response assembly and cytotoxicity assessment of fluoropeptides
By grafting NBD fluorescent molecules onto the polypeptide skeleton, the author further explored the ability of ALP to induce the assembly of fluorinated polypeptides (Figure 4). After incubating with 4T1 cells, the fluoropeptides showed obvious assembly behavior, and the assembly body could stay on the cells for a long time. At the same time, after tail vein injection of fluoride containing polypeptides labeled with near-infrared fluorescence molecules, it was found that the fluoride containing polypeptides gradually gathered in the liver of CLI mice, and the fluorescence intensity reached the peak in 8 hours, which had obvious hysteresis compared with healthy mice.
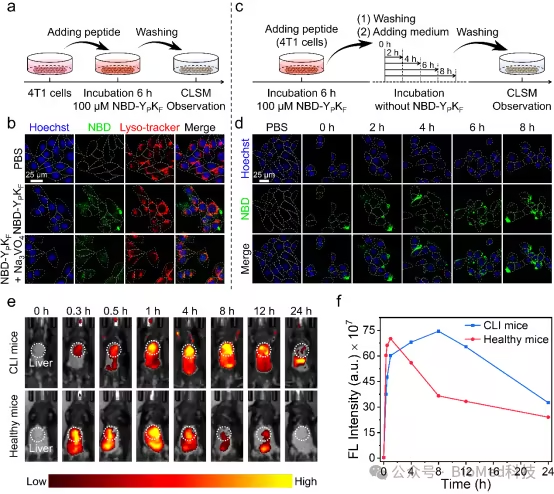
Figure 4 Imaging capability of fluoropeptides
Finally, the author explored the nineteen F NMR urine analysis and treatment capability (Figure 5). Compared with healthy mice, CLI mice showed that nineteen The peak time of F NMR signal was significantly delayed, and nineteen The decline rate of F NMR signal strength is less than that of healthy mice, realizing the nineteen F NMR urine analysis. The author also treated CLI mice with drug modified fluoropeptides. The relevant indexes in the serum of CLI mice recovered to normal levels after treatment, and a series of tissue sections confirmed the gradual recovery of mice.
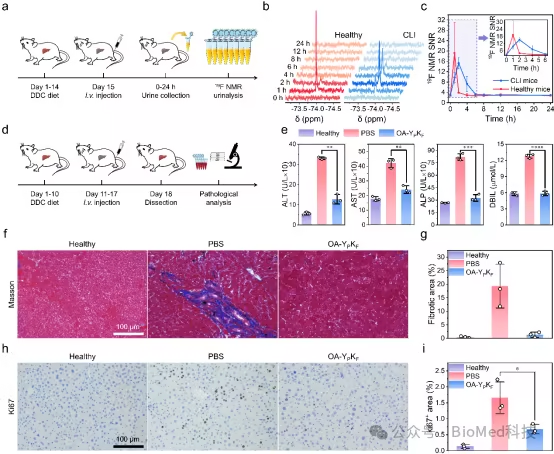
Fig. 5 Fluorine containing polypeptide nineteen F NMR urine analysis and treatment capability
To sum up, researchers have designed a new method for CLI diseases nineteen F NMR urine analysis and enzyme response assembly of drug therapy fluoropeptide molecular therapy platform. Due to the potential substitutability of the enzyme response group (phosphate group in this study) and its functional group in the fluoropeptide molecule, the polypeptide molecular platform has the potential to expand to other disease diagnosis and treatment. The research results are nineteen The peptide molecule integrated with F NMR urine analysis and diagnosis and treatment provides a new design idea.
Beijing University of Chemical Technology Professor Wang Leyu and Professor Xu Suying As the co corresponding author of the paper, Doctor Feng Ruxin He is the first author of this paper. This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22334002, 22322402, 22274007), Beijing Science and Technology Special Project (Z23100002723006), and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (XK2023-19, JD2308, PT2408).
Original link: https://advanced.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202413571
